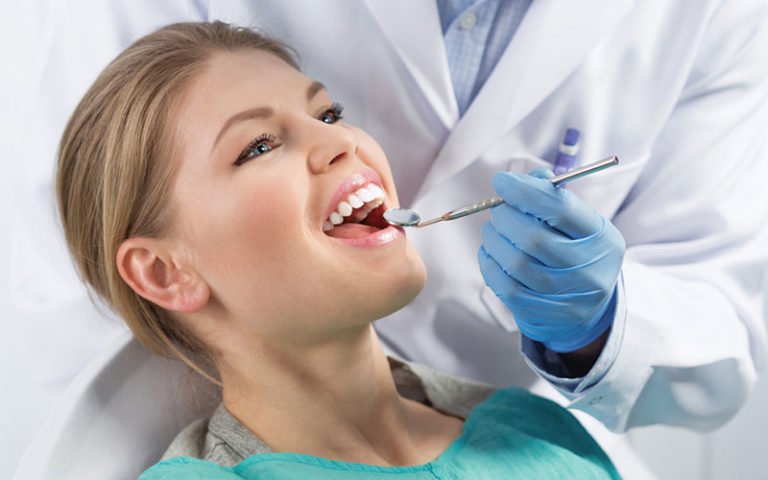
The Importance of Oral and Dental Care: Maintaining a Healthy Smile
Daily Oral Hygiene Routine: Tips for Effective Teeth Cleaning
• Brush your teeth at least twice a day for two minutes using a soft-bristled toothbrush and fluoride toothpaste. Brush all surfaces of your teeth, including the outer, inner, and chewing surfaces. Use gentle, circular motions and pay attention to the gum line.
• Floss daily to remove plaque and food particles from between the teeth and along the gumline. Gently insert the floss between each tooth and move it back and forth in a C-shape motion to clean the sides of the teeth.
• Use an antimicrobial mouthwash to rinse your mouth after brushing and flossing. This helps reduce bacteria, freshens breath, and provides an extra layer of protection against tooth decay and gum disease.
• Limit sugary foods and drinks, as they can contribute to tooth decay. Instead, choose a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and dairy products to support optimal dental health.
• Replace your toothbrush every three to four months or sooner if the bristles become frayed. A worn-out toothbrush may not effectively clean your teeth and gums.
Preventing Dental Issues: Best Practices for Oral Care
• Brush your teeth at least twice a day: Brushing removes plaque, bacteria, and food particles from the teeth and gums. Use a soft-bristled toothbrush and fluoride toothpaste. Ensure you cover all tooth surfaces and brush gently in circular motions.
• Floss daily: Flossing helps remove plaque and debris from between the teeth and along the gum line, where a toothbrush may not reach. Be gentle while flossing to avoid causing gum irritation.
• Maintain a balanced diet: A nutritious diet is essential for dental health. Limit sugary and acidic foods and drinks, as they can contribute to tooth decay. Instead, consume foods rich in vitamins and minerals, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and dairy products.
• Avoid tobacco products: Tobacco use, including smoking and chewing tobacco, can lead to various dental issues, such as gum disease, oral cancer, and tooth discoloration. Quitting tobacco use is beneficial for both oral health and overall well-being.
• Visit your dentist regularly: Regular dental check-ups are crucial for early detection and prevention of dental issues. Schedule dental examinations and professional cleanings at least twice a year, or as recommended by your dentist.
• Wear mouthguards for sports: If you participate in sports or recreational activities, wearing a mouthguard can protect your teeth from injuries and reduce the risk of tooth fractures or loss.
The Role of Nutrition in Dental Health: Foods for a Strong Smile
• Dairy products: Milk, cheese, and yogurt are excellent sources of calcium, which is essential for strong teeth and bones. Calcium helps strengthen tooth enamel, making it more resistant to decay. These dairy products also contain casein, a protein that can help reduce the acidity in the mouth and protect against cavities.
• Crisp fruits and vegetables: Crunchy fruits and vegetables, such as apples, carrots, and celery, can help clean the teeth naturally. Their firm texture stimulates saliva production, which washes away bacteria and food particles. Additionally, they provide vitamins and minerals that contribute to overall oral health.
• Lean proteins: Foods rich in lean proteins, such as chicken, fish, eggs, and legumes, provide essential amino acids that support the growth and repair of oral tissues. These proteins also contain phosphorus, which is important for tooth mineralization and enamel strength.
• Whole grains: Whole grains, such as brown rice, whole wheat bread, and oats, are a healthier choice compared to refined grains. They provide B vitamins and iron, which are essential for gum health and preventing oral sores.
• Water: Water is an essential component of maintaining good oral health. It helps rinse away food particles, promotes saliva production, and keeps the mouth hydrated. Drinking fluoridated water can also help strengthen tooth enamel and protect against cavities.
While incorporating these foods into your diet, it's important to practice good oral hygiene by brushing, flossing, and visiting your dentist regularly. A balanced diet combined with proper oral care can help maintain strong teeth and gums for a healthy smile.
Understanding Gum Disease: Causes, Symptoms, and Prevention
Causes: Gum disease is primarily caused by bacterial plaque, a sticky film that forms on the teeth and gum line. Poor oral hygiene allows plaque to accumulate, leading to gum inflammation and infection. Other factors that contribute to gum disease include smoking, hormonal changes, certain medications, genetic predisposition, and systemic conditions like diabetes.
Symptoms: The early stage of gum disease is known as gingivitis. Common symptoms include red, swollen, or bleeding gums, bad breath, and gum sensitivity. If left untreated, gum disease can progress to advanced stages called periodontitis, which may cause gum recession, tooth mobility, pus formation, and even tooth loss.
Prevention: Preventing gum disease involves maintaining good oral hygiene practices. Brush your teeth at least twice a day, floss daily, and use an antimicrobial mouthwash. Regular dental check-ups and professional cleanings are essential for removing plaque and tartar buildup. Avoid tobacco use, eat a balanced diet, and manage systemic conditions to reduce the risk of gum disease.
By practicing proper oral hygiene, addressing risk factors, and seeking professional dental care, you can significantly reduce the likelihood of gum disease and promote a healthy gum tissue environment.
Choosing the Right Toothbrush and Toothpaste: A Guide for Oral Care
Toothbrush: Opt for a toothbrush with soft bristles to avoid causing damage to the tooth enamel and gums. The size and shape of the brush head should comfortably fit in your mouth and reach all areas of your teeth. Electric toothbrushes with oscillating or rotating heads can provide more effective plaque removal. Replace your toothbrush every three to four months or sooner if the bristles become frayed.
Toothpaste: Look for toothpaste that contains fluoride, a mineral that strengthens tooth enamel and helps prevent tooth decay. Fluoride toothpaste is available in various flavors and formulations to suit individual preferences and dental needs. If you have specific concerns such as sensitivity or gum health, there are specialized toothpaste options available for those conditions.
Personal Preference: Consider your personal preferences when choosing a toothbrush and toothpaste. Some people may prefer a manual toothbrush, while others may find an electric toothbrush more effective and convenient. Similarly, toothpaste flavors and textures vary, so select one that you enjoy using to encourage consistent oral care habits.
Consult Your Dentist: Your dentist can provide personalized recommendations on toothbrushes and toothpaste based on your specific oral health needs. They can also address any concerns or questions you may have about oral care products and help you make an informed decision.
Remember that regular brushing, flossing, and professional dental care are essential for maintaining good oral health, regardless of the toothbrush and toothpaste you choose. Establishing a consistent oral care routine using appropriate oral care products will contribute to a healthy smile and prevent dental issues.
Flossing Techniques: Enhancing Your Oral Hygiene Routine
Proper Technique: Take about 18 inches of dental floss and wrap it around your middle fingers, leaving a couple of inches in between for maneuvering. Hold the floss tightly between your thumbs and index fingers, and gently guide it between each tooth using a back-and-forth sawing motion. Curve the floss into a C-shape against one tooth and slide it beneath the gum line, being careful not to snap it against the gums. Repeat this process for all teeth, using a clean section of floss for each space.
Use Enough Floss: Use enough floss to reach the entire length of each tooth. This ensures effective plaque removal from all surfaces, including the sides of the teeth and just below the gum line.
Be Gentle: Avoid using excessive force while flossing to prevent gum irritation or injury. Gently glide the floss up and down, curving it around the tooth to clean the sides thoroughly. If you experience bleeding or discomfort, it may indicate gum inflammation, and it's important to consult your dentist.
Consider Alternative Flossing Tools: Traditional dental floss may not be suitable for everyone, especially those with dexterity issues or orthodontic appliances. In such cases, alternative flossing tools like floss picks, interdental brushes, or water flossers can be used to effectively clean the teeth. Consult with your dentist to determine which tool is best for you.
Make It a Habit: Flossing should be incorporated into your daily oral hygiene routine. Consistency is key to maintaining optimal oral health. Choose a time of day that works best for you, whether it's before brushing, after meals, or before bedtime, and make flossing a non-negotiable part of your routine.
The Benefits of Mouthwash: Adding an Extra Layer of Protection
Freshens Breath: Mouthwash helps freshen breath by reducing the bacteria that contribute to bad breath. It masks odors temporarily and leaves a refreshing taste in the mouth.
Reduces Plaque and Gingivitis: Certain mouthwashes contain antibacterial ingredients, such as chlorhexidine, or essential oils like thymol or menthol. These ingredients can help reduce plaque buildup and prevent or manage gingivitis, a mild form of gum disease characterized by gum inflammation and bleeding.
Cavity Prevention: Some mouthwashes contain fluoride, which strengthens tooth enamel and helps prevent tooth decay. Using fluoride mouthwash in addition to fluoride toothpaste provides extra protection against cavities.
Soothes Mouth Irritation: Mouthwashes that contain ingredients like aloe vera or chamomile can help soothe mouth irritations, such as canker sores or minor gum injuries. They provide a soothing sensation and promote healing.
Reaches Hard-to-Brush Areas: Mouthwash can reach areas that are difficult to clean with a toothbrush or floss alone. Swishing mouthwash vigorously can help dislodge food particles and bacteria from the back of the mouth and in-between teeth.
Complements Oral Hygiene Routine: Mouthwash should not be used as a substitute for brushing and flossing, but rather as a supplement to your regular oral care routine. It provides an additional step to promote oral health and maintain fresh breath.
It's important to choose a mouthwash that suits your specific needs and consult with your dentist for recommendations. Remember to follow the instructions on the bottle, including the recommended duration and frequency of use. Incorporating mouthwash into your oral care routine can provide added benefits and contribute to a healthier mouth.
Oral Care for Children: Establishing Healthy Habits from an Early Age
Start Early: Begin oral care even before your child's first tooth erupts. Clean their gums gently with a clean, damp cloth or a soft infant toothbrush. As teeth emerge, use an appropriate toothbrush and a smear of fluoride toothpaste, about the size of a grain of rice, to clean their teeth.
Supervise Brushing: Young children may not have the dexterity to brush their teeth effectively. Until they develop the necessary skills, parents should brush their child's teeth, ensuring all surfaces are thoroughly cleaned. As children grow, encourage them to brush on their own while providing supervision and guidance.
Establish a Routine: Set a consistent oral care routine by brushing your child's teeth at least twice a day, in the morning and before bed. Make it a fun and positive experience, using child-friendly toothbrushes, colorful toothpaste, and age-appropriate oral care products.
Encourage a Healthy Diet: Promote a balanced diet for your child's oral health. Limit sugary snacks and drinks, including fruit juices, and encourage healthier options like fruits, vegetables, and dairy products. Drinking water instead of sugary beverages helps rinse away food particles and reduce the risk of cavities.
First Dental Visit: Schedule your child's first dental visit around their first birthday or when the first tooth erupts. Early dental visits allow the dentist to monitor their oral health, provide guidance on oral care, and address any concerns or questions they may have.
Lead by Example: Children learn best by observing their parents or caregivers. Demonstrate good oral care habits by brushing and flossing your teeth regularly. Encourage your child to join in and make it a shared activity.
By establishing a foundation of proper oral care habits early on, you can help your child develop a lifelong commitment to oral health. Regular dental visits, a consistent oral care routine, and a supportive environment contribute to a healthy smile and overall well-being for children.
The Link Between Oral Health and Overall Well-being
Cardiovascular Health: Poor oral health, particularly gum disease, has been linked to an increased risk of cardiovascular conditions such as heart disease, stroke, and clogged arteries. The bacteria and inflammation associated with gum disease can contribute to systemic inflammation and impact cardiovascular health.
Diabetes Management: Diabetes and gum disease have a bidirectional relationship. Poorly controlled diabetes can lead to increased susceptibility to infections, including gum disease. Conversely, gum disease can make it more challenging to control blood sugar levels. Maintaining good oral health is crucial for individuals with diabetes to help manage their condition effectively.
Respiratory Health: Oral health plays a role in respiratory health as well. Poor oral hygiene and untreated gum disease can contribute to respiratory infections, such as pneumonia, as bacteria from the mouth can be inhaled into the lungs.
Pregnancy Complications: Oral health is particularly important during pregnancy. Hormonal changes can increase the risk of gum disease, which has been associated with preterm birth, low birth weight, and other pregnancy complications. Maintaining good oral hygiene and seeking dental care during pregnancy is vital for both the mother's and baby's well-being.
Inflammatory Conditions: Chronic inflammation, as seen in gum disease, has been linked to various systemic conditions, including rheumatoid arthritis, certain cancers, and inflammatory bowel disease. By maintaining oral health, you can help reduce systemic inflammation and potentially lower the risk of these conditions.
Overall Quality of Life: A healthy mouth and smile contribute to confidence, self-esteem, and overall quality of life. Good oral health allows for comfortable eating, speaking, and social interactions, enhancing overall well-being and mental health.
By understanding the connection between oral health and overall well-being, you can prioritize oral care as an essential component of maintaining a healthy body and mind. Regular dental visits, proper oral hygiene, and a healthy lifestyle contribute to both a beautiful smile and improved overall health.
Managing Bad Breath: Causes and Solutions
Causes of Bad Breath: Bad breath can be caused by various factors, including poor oral hygiene, gum disease, cavities, dry mouth, certain foods and beverages (such as onions and coffee), tobacco use, certain medications, and underlying medical conditions like sinus infections or gastrointestinal issues.
Oral Hygiene Practices: Practicing good oral hygiene is crucial for preventing bad breath. Brush your teeth at least twice a day, focusing on the teeth, tongue, and gumline. Don't forget to clean your tongue, as bacteria can accumulate on its surface. Floss daily to remove plaque and food particles from between the teeth. Using an antimicrobial mouthwash can also help reduce bacteria and freshen your breath.
Addressing Underlying Dental Issues: If bad breath persists despite proper oral hygiene, it may be a sign of an underlying dental problem. Gum disease, tooth decay, or infections can contribute to chronic bad breath. Visit your dentist for a thorough examination to identify and address any dental issues that may be causing the problem.
Managing Dry Mouth: Dry mouth, or xerostomia, can contribute to bad breath as saliva helps wash away bacteria in the mouth. Stay hydrated by drinking plenty of water and try chewing sugar-free gum or using saliva substitutes to stimulate saliva production. If dry mouth persists, consult your dentist for further evaluation and potential treatment options.
Avoiding Food Triggers: Certain foods and beverages, such as garlic, onions, and strong spices, can leave lingering odors in the mouth. Limiting or avoiding these foods can help reduce bad breath. Opt for fresh fruits and vegetables, which can help cleanse the mouth and freshen your breath.
Quit Tobacco Use: Tobacco products not only stain teeth but also contribute to bad breath. Quitting smoking or chewing tobacco can significantly improve breath odor and promote overall oral health.
Regular Dental Check-ups: Regular dental visits are important for maintaining oral health and addressing any concerns related to bad breath. Your dentist can help identify the underlying causes and provide appropriate treatment or recommendations.
Dealing with Tooth Sensitivity: Tips for Sensitive Teeth
Use Desensitizing Toothpaste: Desensitizing toothpaste, specifically formulated for sensitive teeth, can provide relief. These toothpaste contain ingredients that help block nerve signals and reduce tooth sensitivity over time. Use the toothpaste as directed and be patient, as it may take several applications before you notice a significant improvement.
Practice Proper Brushing Techniques: Brushing with excessive force or using a hard-bristled toothbrush can aggravate tooth sensitivity. Opt for a soft-bristled toothbrush and brush gently using small, circular motions. Avoid scrubbing back and forth, as this can wear down tooth enamel and contribute to sensitivity. Also, be sure to use toothpaste that is specifically designed for sensitive teeth.
Avoid Acidic Foods and Drinks: Acidic foods and beverages can erode tooth enamel and worsen tooth sensitivity. Limit your consumption of acidic items such as citrus fruits, tomatoes, soda, and sports drinks. If you do consume acidic foods or beverages, rinse your mouth with water afterward to help neutralize the acid.
Use a Fluoride Mouthwash: Using a fluoride mouthwash can help strengthen tooth enamel and reduce tooth sensitivity. Rinse your mouth with a fluoride mouthwash after brushing your teeth, following the instructions on the product label.
Address Teeth Grinding: Teeth grinding, also known as bruxism, can contribute to tooth sensitivity. If you grind your teeth, especially during sleep, consider wearing a mouthguard or splint to protect your teeth from excessive force. Consult with your dentist to determine the best solution for your specific needs.
Visit Your Dentist: If tooth sensitivity persists or worsens, it's important to seek professional dental care. Your dentist can evaluate the cause of your sensitivity and recommend appropriate treatments. They may suggest procedures such as dental bonding, fluoride varnishes, or in-office desensitizing treatments to alleviate the sensitivity.
Managing tooth sensitivity requires a combination of proper oral hygiene practices and professional dental care. By implementing these tips and seeking guidance from your dentist, you can reduce tooth sensitivity and enjoy a more comfortable eating and drinking experience.
Oral Care for Seniors: Addressing Age-related Dental Concerns
Regular Dental Check-ups: Regular dental visits are essential for seniors to monitor their oral health. Schedule dental check-ups at least twice a year or as recommended by your dentist. These visits allow for early detection and treatment of dental issues that may arise.
Dry Mouth Management: Dry mouth, or xerostomia, is a common issue for seniors and can lead to various oral health problems. Stay hydrated, chew sugar-free gum, or use saliva substitutes to alleviate dry mouth symptoms. Your dentist may also recommend products that can help stimulate saliva production.
Proper Denture Care: Seniors who wear dentures should ensure they are cleaned and maintained properly. Remove and clean dentures daily using denture cleansers or mild soapy water. Also, make sure to clean your gums, tongue, and any remaining natural teeth.
Medication Review: Many seniors take multiple medications, some of which can affect oral health. Certain medications may cause dry mouth, gum problems, or contribute to tooth decay. Discuss your medications with your dentist to identify any potential concerns and find ways to mitigate their effects.
Prevention of Gum Disease: Gum disease can be more prevalent in seniors due to factors such as reduced saliva flow and age-related changes in oral tissues. Practice good oral hygiene, including brushing twice a day, flossing, and using antimicrobial mouthwash. Regular professional cleanings and gum evaluations are also important.
Oral Cancer Screenings: Seniors are at a higher risk of developing oral cancer. Regular oral cancer screenings during dental check-ups are crucial for early detection. Your dentist will examine your mouth, tongue, and throat for any signs of abnormalities.
Maintaining a Healthy Diet: A nutritious diet plays a significant role in maintaining oral health. Seniors should consume a well-balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and dairy products to provide the necessary nutrients for strong teeth and gums.
Dental Visits and Check-ups: The Importance of Regular Examinations
Early Detection of Dental Issues: Dental check-ups allow dentists to identify dental problems at their earliest stages. Early detection means early intervention, which can prevent the progression of issues such as cavities, gum disease, or tooth infections. It helps avoid more extensive and costly dental treatments down the line.
Professional Cleaning: During dental visits, dental hygienists will perform professional cleanings to remove plaque, tartar, and surface stains. Even with regular brushing and flossing at home, some areas may be difficult to clean thoroughly. Professional cleanings help maintain a clean and healthy mouth.
Oral Cancer Screenings: Regular dental check-ups include oral cancer screenings. Dentists are trained to identify signs of oral cancer or precancerous conditions. Early detection of oral cancer significantly improves treatment outcomes.
Individualized Treatment Plans: Dental check-ups allow dentists to assess your oral health and create personalized treatment plans. They can address specific concerns, provide preventive measures, and recommend appropriate treatments tailored to your needs.
Education and Guidance: Dentists and dental hygienists provide valuable education and guidance during dental visits. They can offer advice on proper oral hygiene techniques, recommend oral care products, and answer any questions you may have about your oral health.
Monitoring Overall Health: Dental health is closely linked to overall health. Certain medical conditions, medications, or lifestyle habits can affect your oral health. Regular dental visits allow dentists to monitor any changes and coordinate with other healthcare providers if necessary.
By prioritizing regular dental visits and check-ups, you can proactively maintain your oral health, prevent dental problems, and ensure early intervention if any issues arise. It's recommended to schedule dental check-ups at least twice a year or as advised by your dentist, depending on your specific dental needs.
Common Dental Emergencies: How to Handle Urgent Oral Care
Toothache: If you experience a toothache, rinse your mouth with warm saltwater to reduce inflammation. Gently floss around the affected tooth to remove any trapped debris. Avoid placing aspirin directly on the gums or tooth, as it can irritate. Contact your dentist for an appointment to determine the cause of the toothache and receive appropriate treatment.
Knocked-Out Tooth: If a permanent tooth is knocked out, try to re-implant it by carefully rinsing it under water and placing it back into the socket, holding it by the crown. If this isn't possible, store the tooth in a container of milk or saliva and seek immediate dental care. Time is crucial for the successful reattachment of the tooth, so act quickly.
Chipped or Fractured Tooth: Rinse your mouth with warm water to clean the area. If you can find the broken tooth fragment, place it in milk or saliva. Apply a cold compress to the affected area to reduce swelling. Contact your dentist for an appointment as soon as possible to evaluate the extent of the damage and determine the appropriate treatment.
Lost Filling or Crown: If a filling or crown becomes loose or falls out, clean the affected tooth and try to reinsert the crown temporarily using dental adhesive or toothpaste. Avoid chewing on the side with the missing restoration and contact your dentist for an appointment to have it properly replaced.
Object Stuck Between Teeth: Gently try to remove the object using dental floss. Do not use sharp or pointed objects that could cause injury. If you're unable to remove it, contact your dentist for assistance. Avoid forcing the object, as it may damage the gums or teeth.
In any dental emergency, it's important to seek professional dental care promptly. Contact your dentist for immediate attention or, if the emergency occurs outside of regular office hours, visit an emergency dental clinic. Acting quickly can help preserve your oral health and prevent complications.
Our Patients' Comments
DANIELO JASON
6 PACK j’avais du mal a faire du sport et de suivre des regimes alimentaires mais sans resultat alors cette annee je me suis dirigé vers REFERENCE ESTHETIQUE en turquie et vraiment je me sens pret pour l’été comme jamais. Merci de m’avoir redonner confiance en moi.
BAHIJA BELHAJ
MEME KUCULTME La clinique est bien situé par rapport au metrobus station, les guichets bancaire sont juste a coté, le market est dont vous aurez besoin, j’étais labas pour faire une reduction mammaire, je ne me suis jamais senti bien dans ma peau jusqu’au jour ou j’ai décidé de me faire opéré chez REFERENCE ESTHETIQUE a Istanbul, Merci






